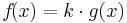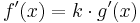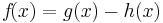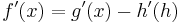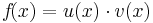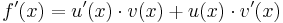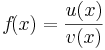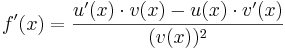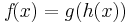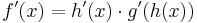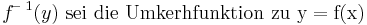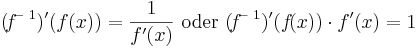|
|
| Zeile 58: |
Zeile 58: |
| | | | |
| | <math>(\!f\!^-\,^1)'(f(x))=\frac{1}{f'(x)}\ \mathrm{oder}\ (\!f\!^-\,^1)'(f\!(x)) \cdot f\!\,'(x)=1</math> | | <math>(\!f\!^-\,^1)'(f(x))=\frac{1}{f'(x)}\ \mathrm{oder}\ (\!f\!^-\,^1)'(f\!(x)) \cdot f\!\,'(x)=1</math> |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == Beispiele ==
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Summenregel ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==== Beispiel ====
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>f\!(x)=3x^2+5x</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | => <math>f\!\,'(x)=(3x^2+5x)'=(3x^2)'+(5x)'=6x+5</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Produktregel ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==== Beispiel 1 ====
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>f\!(x)=(4x^3-2x+1) \cdot (x^2-2x+5)</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>\mathrm{Bestandteile}\ \begin{cases}
| |
| − | u(x)=4x^3-2x+1\\
| |
| − | v(x)=x^2-2x+5
| |
| − | \end{cases}</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>\mathrm{Ableitungen\ der\ Bestandteile}\ \begin{cases}
| |
| − | u'(x)=12x^2-2\\
| |
| − | v'(x)=2x-2
| |
| − | \end{cases}</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>f\!\,'(x)=(12x^2-2) \cdot (x^2-2x+5)+(4x^3-2x+1) \cdot (2x-2)</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>f\!\,'(x)=12x^4-24x^3+60x^2-2x^2+4x-10+8x^4-8x^3-4x^2+4x+2x-2</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>f\!\,'(x)=\boldsymbol{\underline{\underline{20x^4-32x^3+54x^2+10x-12}}}</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==== Beispiel 2 ====
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>f\!(x)=\sin(x) \cdot \cos(x)</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>\mathrm{Bestandteile}\ \begin{cases}
| |
| − | u(x)=\sin(x)\\
| |
| − | v(x)=\cos(x)
| |
| − | \end{cases}</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>\mathrm{Ableitungen\ der\ Bestandteile}\ \begin{cases}
| |
| − | u'(x)=\cos(x)\\
| |
| − | v'(x)=-\sin(x)
| |
| − | \end{cases}</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>f\!\,'(x)=\cos(x) \cdot \cos(x)+\sin(x) \cdot (-\sin(x))</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>f\!\,'(x)=\boldsymbol{\underline{\underline{\cos^2(x)-\sin^2(x)}}}</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==== Beispiel 3 ====
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>f\!(x)=x^n \cdot e^{x}</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>\mathrm{Bestandteile}\ \begin{cases}
| |
| − | u(x)=x^n\\
| |
| − | v(x)=e^{x}
| |
| − | \end{cases}</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>\mathrm{Ableitungen\ der\ Bestandteile}\ \begin{cases}
| |
| − | u'(x)=n \cdot x^{n-1}\\
| |
| − | v'(x)=e^{x}
| |
| − | \end{cases}</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>f\!\,'(x)=(n \cdot x^{n-1}) \cdot (e^{x})+(x^n) \cdot (e^{x})</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>f\!\,'(x)=\boldsymbol{\underline{\underline{x^{n-1} \cdot e^{x} \cdot (n+x)}}}</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Quotientenregel ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==== Beispiel ====
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>f\!(x)=\frac{1-2x}{4+3x^2}</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>\mathrm{Bestandteile}\ \begin{cases}
| |
| − | u(x)=1-2x\\
| |
| − | v(x)=4+3x^2
| |
| − | \end{cases}</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>
| |
| − | \mathrm{Ableitungen\ der\ Bestandteile}
| |
| − | \begin{cases}
| |
| − | u'(x)=-2\\
| |
| − | v'(x)=6x
| |
| − | \end{cases}
| |
| − | </math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>f\!\,'(x)=\frac{(-2) \cdot (4+3x^2)-(1-2x) \cdot (6x)}{(4+3x^2)^2}</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>f\!\,'(x)=\boldsymbol{\underline{\underline{\frac{6x^2-6x-8}{(4+3x^2)^2}}}}</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === Kettenregel ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==== Beispiel ====
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>f\!(x)=e^{(x^2+2x)}</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>\mathrm{Bestandteile}\ \begin{cases}
| |
| − | u(x)=e^x\\
| |
| − | v(x)=x^2+2x
| |
| − | \end{cases}</math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>
| |
| − | \mathrm{Ableitungen\ der\ Bestandteile}
| |
| − | \begin{cases}
| |
| − | u'(x)=e^x\\
| |
| − | v'(x)=2x+2
| |
| − | \end{cases}
| |
| − | </math>
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <math>f\!\,'(x)=\boldsymbol{\underline{\underline{e^{(x^2+2x)} \cdot (2x+2)}}}</math>
| |