Ganzrationale Funktionen.: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Aus KAS-Wiki
Franca (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
Franca (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
||
| Zeile 5: | Zeile 5: | ||
n = Grad des Polynoms | n = Grad des Polynoms | ||
| − | Definitionsbereich: | + | |
| + | ==== Definitionsbereich: ==== | ||
* <math>n\in\N</math> | * <math>n\in\N</math> | ||
* a<sub>n</sub> <math>\not=</math> 0 | * a<sub>n</sub> <math>\not=</math> 0 | ||
| − | Bestimmung einer ganzrationalen Funktion in Sachzusammenhängen: | + | |
| + | ==== Bestimmung einer ganzrationalen Funktion in Sachzusammenhängen: ==== | ||
* lineares Gleichungssystem aufstellen und lösen | * lineares Gleichungssystem aufstellen und lösen | ||
| Zeile 16: | Zeile 18: | ||
* Bedingung: n + 1 Bedingungen sind nötig | * Bedingung: n + 1 Bedingungen sind nötig | ||
| − | |||
| − | p/q-Formel: | + | ==== 1.) Nullstellen der Funktion:<br /><br /> f(x)=0 ==== |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == p/q-Formel: == | ||
| + | |||
f(x) = <math>x^2</math> + px + q = 0 | f(x) = <math>x^2</math> + px + q = 0 | ||
Version vom 14. Dezember 2009, 10:47 Uhr
Inhaltsverzeichnis |
Ganzrationale Funktionen
f(x) = anxn + an-1xn-1 + ... + a1x + a0
n = Grad des Polynoms
Definitionsbereich:
-
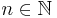
- an
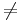 0
0
Bestimmung einer ganzrationalen Funktion in Sachzusammenhängen:
- lineares Gleichungssystem aufstellen und lösen
- Koordinatensystem auswählen
- Bedingung: n + 1 Bedingungen sind nötig
1.) Nullstellen der Funktion:
f(x)=0
p/q-Formel:
f(x) = 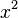 + px + q = 0
+ px + q = 0
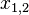 =
= 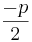
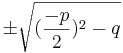
- f(x)= ax2 + bx + c

