Affine Abbildungen
Aus KAS-Wiki
Version vom 7. Dezember 2009, 08:54 Uhr von Helen H. (Diskussion | Beiträge)
Definition:
Eine geradentreue und umkehrbare geometrische Abbildung der Ebene auf sich selbst nennt man eine affine Abbildung oder Affinität.
Die affine Abbildung bildet ein neues Koordinatensystem.
Die einzelnen Spalten der Matrix dürfen nicht linear abhängig sein.
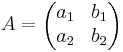
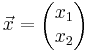

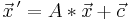
LGS:
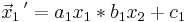
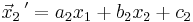
| Abbildung | Flächeninhalt | Fixpunkte, Fixgeraden | Matrixdarstellung |
| Spiegelung | A bleibt gleich | (0/0) Spiegelgerade (Fixgerade) | 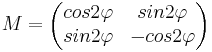
|
| zentrische Streckung | 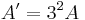 |
(0/0) x-und y-Achse jede Gerade 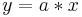 |
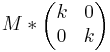
|
| Drehung | A bleibt gleich | (0/0) | 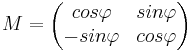
|
| Skalierung | 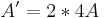 |
(0/0) x- und y-Achse | |
| Scherung | 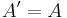 |
(0/0) x- oder y-Achse |

